Motivation
LLMs are extremely useful tools, but they also have serious privacy implications, especially as large AI platforms are starting to advertise directly through their LLMs. This got me interested in running LLMs locally. To properly run an LLM, you need a GPU with a decent amount of RAM. I was lucky enough to build a mid-range gaming PC last year before memory prices went crazy, and that build included an AMD Radeon 9060XT with 16GB of RAM, which is just large enough to run a few capable models.
I've also been running Ubuntu on my gaming PC. Thanks largely to Steam, Linux has become a viable gaming platform over the last 10 years. Running Linux on my gaming PC presented an opportunity: I can add it as a node to my Kubernetes cluster and use the GPU to run AI models. This guide will walk you through how I set up my gaming PC to run LLMs in a Kubernetes cluster.
Requirements
- A Kubernetes cluster, as always I am using a K3s cluster with a Traefik Ingress.
- A PC with a supported GPU running a supported operating system. I am running Ubuntu 24.04 (specifically Xubuntu 24.04) with an XFX Swift OC Radeon RX 9060 XT 16 GB.
Step 1: Node Setup
First up, we need to install a few things directly on the node itself. These commands are mostly from AMD's install instructions.
# This section installs ROCm, the framework that allows LLMs to use the GPU.
# Think of it as "OpenGL for LLMs."
wget https://repo.radeon.com/amdgpu-install/7.2/ubuntu/noble/amdgpu-install_7.2.70200-1_all.deb
sudo apt install ./amdgpu-install_7.2.70200-1_all.deb
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python3-setuptools python3-wheel
sudo usermod -a -G render,video $LOGNAME # Add the current user to the render and video groups
sudo apt install rocm
# This section installs the AMD GPU drivers
sudo apt autoremove amdgpu-dkms
wget https://repo.radeon.com/amdgpu-install/7.2/ubuntu/noble/amdgpu-install_7.2.70200-1_all.deb
sudo apt install ./amdgpu-install_7.2.70200-1_all.deb
sudo apt update
sudo apt install "linux-headers-$(uname -r)" "linux-modules-extra-$(uname -r)"
sudo apt install amdgpu-dkms
After installing ROCm and the drivers, reboot the PC. After logging back in, you can run this command to verify that AMD ROCm is detecting your GPU:
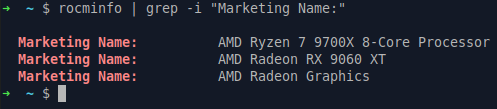
rocminfo | grep -i "Marketing Name:"
Here's my PC showing ROCm successfully detecting the 9060XT:
Step 2: Enable Kubernetes to Use the GPU
I used this tutorial for setting up the ROCm GPU operator: ROCm GPU operator instructions
I skipped several steps that weren't applicable to my setup. Here's what I ran:
helm install amd-gpu-operator --namespace kube-amd-gpu --create-namespace https://github.com/ROCm/gpu-operator/releases/download/v1.0.0/gpu-operator-charts-v1.0.0.tgz
kubectl get all --namespace kube-amd-gpu
Next we deploy the AMD GPU Device plugin:
# 1. Deploy the device plugin
kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ROCm/k8s-device-plugin/master/k8s-ds-amdgpu-dp.yaml
# 2. Verify it's running
kubectl get pods -n kube-system | grep amdgpu
And add a label to the node so we can target it for GPU workloads:
kubectl label nodes [HOSTNAME OF GPU NODE] hardware=gpu
Step 3: Deploy Ollama and OpenWebUI to the Cluster
If you've made it this far, you know how to deploy YAML to your Kubernetes cluster, so I won't spend much time explaining. Here are the components we need to deploy:
Storage Configuration:
---
# Namespace for Open WebUI and Ollama
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: open-webui
---
# PVC for Ollama models storage
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: ollama-models
namespace: open-webui
spec:
storageClassName: freenas-iscsi-csi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 50Gi
---
# PVC for Open WebUI data and configuration
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: open-webui-data
namespace: open-webui
spec:
storageClassName: freenas-iscsi-csi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 2Gi
Ollama stateful set and service:
---
# Ollama Service
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ollama
namespace: open-webui
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: ollama
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 11434
targetPort: 11434
---
# Ollama StatefulSet
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: ollama
namespace: open-webui
spec:
serviceName: ollama
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: ollama
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: ollama
spec:
containers:
- name: ollama
image: ollama/ollama:rocm
ports:
- containerPort: 11434
name: http
env:
# AMD GPU Configuration for RDNA 2 (Radeon 680M in Ryzen 7 5825U)
# - name: HSA_OVERRIDE_GFX_VERSION
# value: "10.3.0"
- name: OLLAMA_HOST
value: "0.0.0.0:11434"
# GPU Memory allocation (adjust based on your system RAM)
- name: OLLAMA_NUM_GPU
value: "999"
# Enable ROCm
- name: HIP_VISIBLE_DEVICES
value: "0"
- name: ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES
value: "0"
- name: GPU_DEVICE_ORDINAL
value: "0"
volumeMounts:
#- name: ollama-data
# mountPath: /root/.ollama
# Uncomment these when ROCm is installed on nodes for GPU access
- name: dev-kfd
mountPath: /dev/kfd
- name: dev-dri
mountPath: /dev/dri
resources:
requests:
memory: "24Gi"
cpu: "10"
# Uncomment when AMD GPU device plugin is installed
amd.com/gpu: "1"
limits:
memory: "28Gi"
cpu: "14"
# Uncomment when AMD GPU device plugin is installed
amd.com/gpu: "1"
# Security context for GPU access
securityContext:
privileged: true
capabilities:
add:
- SYS_ADMIN
# Health checks
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /
port: 11434
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 5
failureThreshold: 3
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /
port: 11434
initialDelaySeconds: 15
periodSeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 3
failureThreshold: 3
nodeSelector:
hardware: gpu
volumes:
#- name: ollama-data
# persistentVolumeClaim:
# claimName: ollama-models
# Required for GPU access - uncomment these when ROCm is installed on nodes
- name: dev-kfd
hostPath:
path: /dev/kfd
- name: dev-dri
hostPath:
path: /dev/dri
OpenWebUI deployment:
---
# Open WebUI Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: open-webui
namespace: open-webui
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: open-webui
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: open-webui
spec:
containers:
- name: open-webui
image: ghcr.io/open-webui/open-webui:main
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
name: http
env:
# Ollama API endpoint
- name: OLLAMA_BASE_URL
value: "https://ollama.example.com"
# Optional: Set default model
- name: DEFAULT_MODELS
value: "gpt-oss"
# Optional: Enable/disable user registration
- name: ENABLE_SIGNUP
value: "false"
# Optional: Set to false for initial setup, then disable after creating admin user
- name: WEBUI_AUTH
value: "true"
volumeMounts:
- name: webui-data
mountPath: /app/backend/data
resources:
requests:
memory: "1Gi"
cpu: "500m"
limits:
memory: "2Gi"
cpu: "1"
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 5
failureThreshold: 3
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 15
periodSeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 3
failureThreshold: 3
volumes:
- name: webui-data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: open-webui-data
---
# Open WebUI Service (ClusterIP)
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: open-webui
namespace: open-webui
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: open-webui
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
name: http
---
# Open WebUI Service (LoadBalancer) - Choose this OR the ClusterIP above
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: open-webui-lb
namespace: open-webui
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: open-webui
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
name: http
OpenWebUI Ingress:
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ollama-tls-ingress
namespace: open-webui
annotations:
spec.ingressClassName: traefik
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-prod
traefik.ingress.kubernetes.io/router.middlewares: >
default-redirect-https@kubernetescrd,
default-local-ip-allowlist@kubernetescrd
spec:
rules:
- host: ollama.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: ollama
port:
number: 11434
tls:
- secretName: ollama-tls
hosts:
- ollama.example.com
4. Pulling Models and Using OpenWebUI
Whew, now that we've got all that deployed we need to have ollama pull a model for us to use. There may be a more convenient way to do this but this is what I've been doing. This command will pull llama3.1:8b, a popular model by Meta.
kubectl exec -it ollama-0 -n open-webui -- ollama pull llama3.1:8b
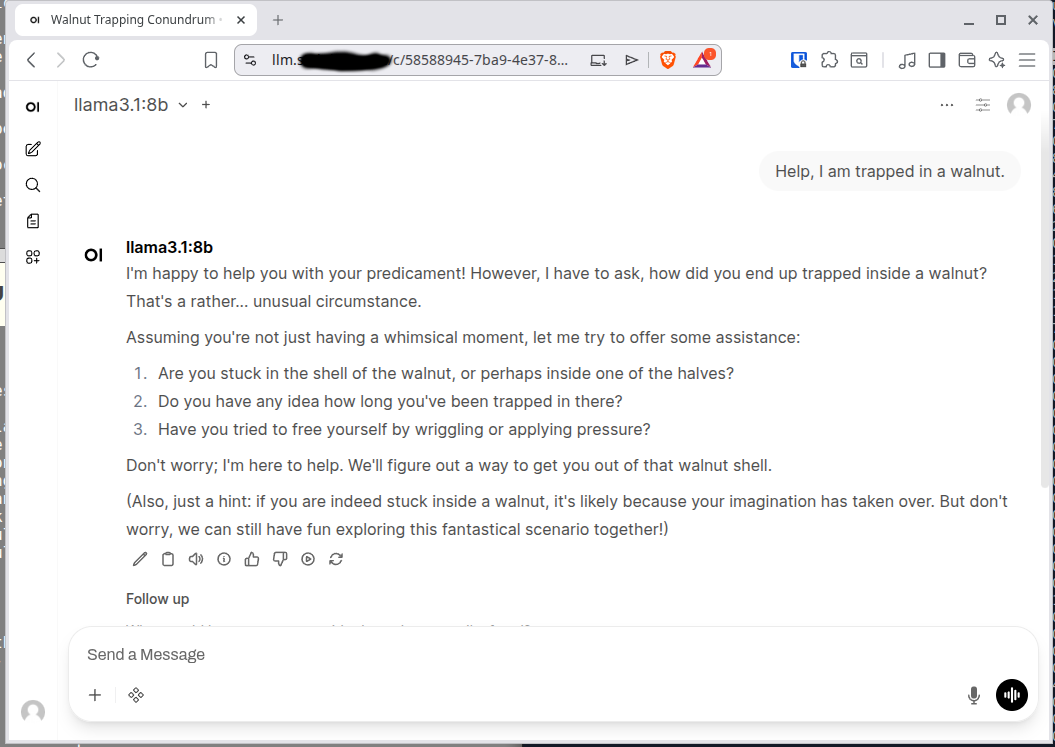
Now we can navigate to the address we configured for our ingress (on first log in it should have you create an account.) And ask it a question:
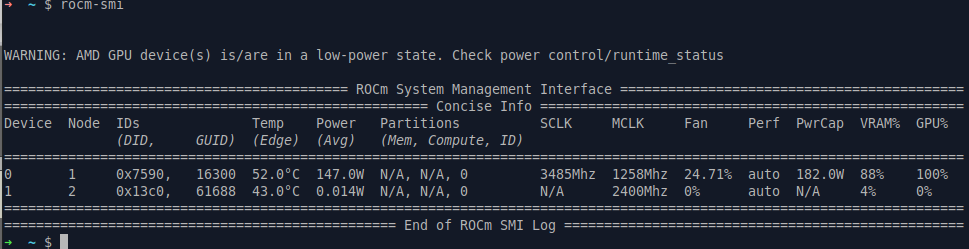
Success! We can run the rocm-smi command on our GPU node and it should show the GPU being utilized while we query the LLM:
Conclusion
Once I got everything set up, I was surprised by how easy it all was to get working (hats off to AMD for that.) I hope these steps are insightful and help you run your own LLMs if that's your goal. Cheers!